I-SURF 2017 Documentation for NVIDIA Jetson TX2

This post is the result of my 2-month project with NVIDIA Jetson TX2.
It contains how to do the initial setup, what is DVFS, about NVPModel, how to measure power performance, and how to use custom benchmark code.
Initial Setup (Click here to view related post)
We can download SDK(JetPack) from this site.
After that, we can do the initial setup for NVIDIA Jetson TX2.
Put JetPack script into specific directory and type following commands.
1
2
$ chmod +x JetPack-L4T-3.0-linux-x64.run
$ ./JetPack-L4T-3.0-linux-x64.run
After that, you can see below GUI window.
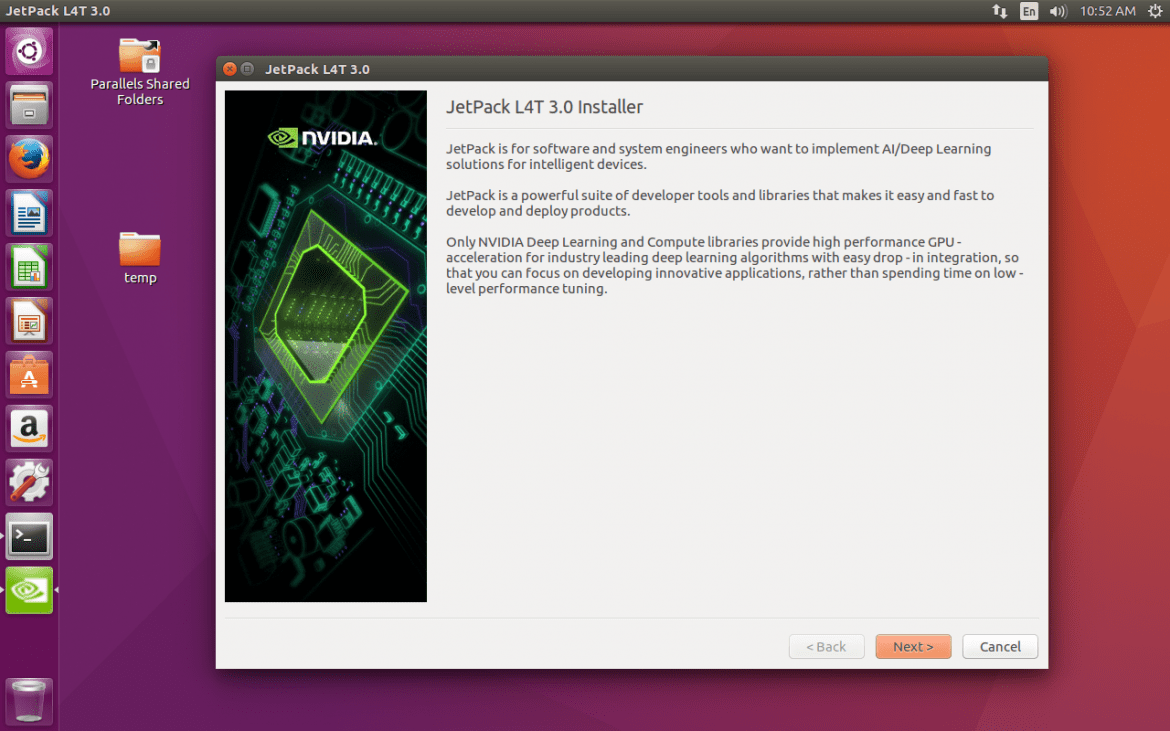
Press next, and select NVIDIA Jetson TX2 and press next again.
Then, you can see the list of available software.
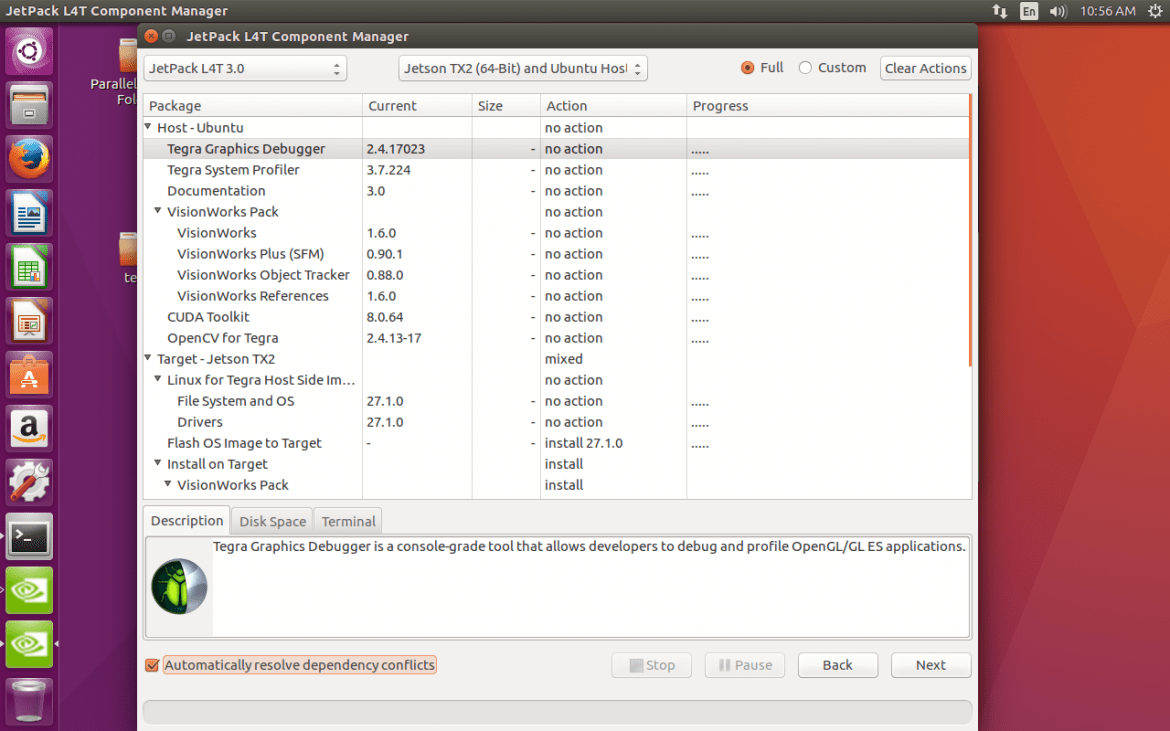
Select what you want to install, and press next. Please note that your computer and NVIDIA Jetson TX2 must be connected to the internet to the same router.
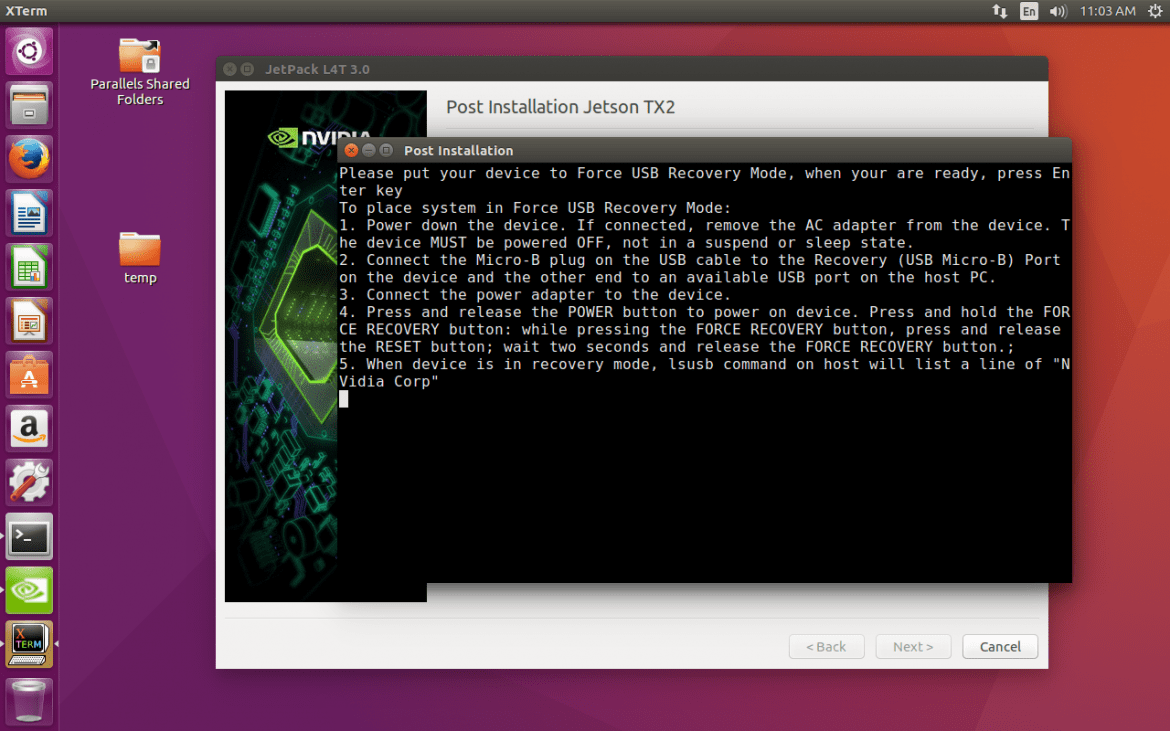
Prepare your device to recovery mode and just wait. SDK will automatically setup your device.
About DVFS (Click here to view related post)
DVFS is an acronym of Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling. You can see details in below links.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dynamic_voltage_scaling
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dynamic_frequency_scaling
- http://processors.wiki.ti.com/index.php/DVFS_User_Guide
About NVPModel (Click here to view related post)
NVPModel makes it easy to adjust the clock of CPU or GPU cores and on/off state. You can use “nvpmodel” command and just type 1-line command to change device operation state.
You can see details on this site.
About Power Monitoring (Click here to view related post)
NVIDIA Jetson TX2 supports power monitoring via I2C bus.
We can check each value using sysfs.
TX2 has 12 PMUs.
Please check this post too.
You can check PMUs in below directories.
1
2
3
4
/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0040/iio_device
/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0041/iio_device
/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0042/iio_device
/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0043/iio_device
Each directory has 3 rails, which are connected to each sensor.
To check the name of each sensor, you can read the “rail_name_N” file in the corresponding directory.
(Please note that N is 0, 1, or 2.)
Each sensor provides voltage(mV), current(mA), and power(mW).
You can get these information by reading “in_currentN_input”, “in_voltageN_input”, and “in_powerN_input”.
(Please note that N is 0, 1, or 2.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <limits>
#include <functional>
#include <chrono>
#include <tuple>
#include <thread>
#include <atomic>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/gpu/gpu.hpp>
#define NUM_OF_ITERATION 30
using namespace std;
using namespace chrono;
inline void prepareBenchmark(string &left_img_path, string &right_img_path);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if(argc != 3) {
cout << "Usage : <executable> <left_img> <right_img>" << endl;
return -1;
}
/* directory path */
string left_img_path = argv[1];
string right_img_path = argv[2];
prepareBenchmark(left_img_path, right_img_path);
return 0;
}
inline void prepareBenchmark(string &left_img_path, string &right_img_path) {
/* Load images */
cv::Mat left_img = cv::imread(left_img_path, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
cv::Mat right_img = cv::imread(right_img_path, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
/* Prepare for GPU */
cv::gpu::GpuMat left_img_gpu; left_img_gpu.upload(left_img);
cv::gpu::GpuMat right_img_gpu; right_img_gpu.upload(right_img);
/* Intended to check if each sequence is finished. */
atomic_bool is_sequence_finished;
/* Store the result of each sequence. */
tuple<double, double, double, double, double, double, double, double, double, double, double, double> power_results;
auto powerCheckFunc = [&is_sequence_finished, &power_results]() -> void {
double VDD_SYS_GPU = 0.0;
double VDD_SYS_SOC = 0.0;
double VDD_4V0_WIFI = 0.0;
double VDD_IN = 0.0;
double VDD_SYS_CPU = 0.0;
double VDD_SYS_DDR = 0.0;
double VDD_MUX = 0.0;
double VDD_5V0_IO_SYS = 0.0;
double VDD_3V3_SYS = 0.0;
double VDD_3V3_IO_SLP = 0.0;
double VDD_1V8_IO = 0.0;
double VDD_3V3_SYS_M2 = 0.0;
unsigned int loop_count = 0;
string value_read_path;
double value = 0.0;
while(!is_sequence_finished.load()) {
loop_count++;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0040/iio_device/in_power0_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_SYS_GPU(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_SYS_GPU >> value; ifs_VDD_SYS_GPU.close();
VDD_SYS_GPU += value;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0040/iio_device/in_power1_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_SYS_SOC(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_SYS_SOC >> value; ifs_VDD_SYS_SOC.close();
VDD_SYS_SOC += value;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0040/iio_device/in_power2_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_4V0_WIFI(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_4V0_WIFI >> value; ifs_VDD_4V0_WIFI.close();
VDD_4V0_WIFI += value;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0041/iio_device/in_power0_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_IN(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_IN >> value; ifs_VDD_IN.close();
VDD_IN += value;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0041/iio_device/in_power1_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_SYS_CPU(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_SYS_CPU >> value; ifs_VDD_SYS_CPU.close();
VDD_SYS_CPU += value;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0041/iio_device/in_power2_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_SYS_DDR(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_SYS_DDR >> value; ifs_VDD_SYS_DDR.close();
VDD_SYS_DDR += value;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0042/iio_device/in_power0_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_MUX(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_MUX >> value; ifs_VDD_MUX.close();
VDD_MUX += value;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0042/iio_device/in_power1_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_5V0_IO_SYS(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_5V0_IO_SYS >> value; ifs_VDD_5V0_IO_SYS.close();
VDD_5V0_IO_SYS += value;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0042/iio_device/in_power2_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_3V3_SYS(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_3V3_SYS >> value; ifs_VDD_3V3_SYS.close();
VDD_3V3_SYS += value;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0043/iio_device/in_power0_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_3V3_IO_SLP(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_3V3_IO_SLP >> value; ifs_VDD_3V3_IO_SLP.close();
VDD_3V3_IO_SLP += value;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0043/iio_device/in_power1_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_1V8_IO(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_1V8_IO >> value; ifs_VDD_1V8_IO.close();
VDD_1V8_IO += value;
value_read_path = "/sys/devices/3160000.i2c/i2c-0/0-0043/iio_device/in_power2_input";
ifstream ifs_VDD_3V3_SYS_M2(value_read_path, ifstream::in); ifs_VDD_3V3_SYS_M2 >> value; ifs_VDD_3V3_SYS_M2.close();
VDD_3V3_SYS_M2 += value;
/* 0.1 second cooling time. */
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
VDD_SYS_GPU /= (double)loop_count;
VDD_SYS_SOC /= (double)loop_count;
VDD_4V0_WIFI /= (double)loop_count;
VDD_IN /= (double)loop_count;
VDD_SYS_CPU /= (double)loop_count;
VDD_SYS_DDR /= (double)loop_count;
VDD_MUX /= (double)loop_count;
VDD_5V0_IO_SYS /= (double)loop_count;
VDD_3V3_SYS /= (double)loop_count;
VDD_3V3_IO_SLP /= (double)loop_count;
VDD_1V8_IO /= (double)loop_count;
VDD_3V3_SYS_M2 /= (double)loop_count;
power_results = make_tuple(VDD_SYS_GPU, VDD_SYS_SOC, VDD_4V0_WIFI, VDD_IN,
VDD_SYS_CPU, VDD_SYS_DDR, VDD_MUX, VDD_5V0_IO_SYS,
VDD_3V3_SYS, VDD_3V3_IO_SLP, VDD_1V8_IO, VDD_3V3_SYS_M2);
};
is_sequence_finished = false;
/* Start power measuring thread. */
thread power_measure_thread(powerCheckFunc);
/* Check the time at begin. */
high_resolution_clock::time_point t1 = high_resolution_clock::now();
/* Loop count check. */
atomic_int loop_count;
/* CPU Thread Function */
auto executeSBM_CPU = [&loop_count, &left_img, &right_img]() {
cv::Mat result_img = cv::Mat(left_img.rows, right_img.cols, CV_8UC1);
while(loop_count.fetch_add(1) < NUM_OF_ITERATION) {
cv::StereoBM stereo_bm;
stereo_bm(left_img, right_img, result_img);
}
};
/* GPU Thread Function */
auto executeSBM_GPU = [&loop_count, &left_img_gpu, &right_img_gpu]() {
cv::gpu::GpuMat result_img_gpu = cv::gpu::GpuMat(left_img_gpu.rows, right_img_gpu.cols, CV_8UC1);
while(loop_count.fetch_add(1) < NUM_OF_ITERATION) {
cv::gpu::StereoBM_GPU stereo_bm_gpu;
stereo_bm_gpu(left_img_gpu, right_img_gpu, result_img_gpu);
}
};
/* Set initial value (==0) of loop count. */
loop_count.store(0);
/* Start each thread. */
thread cpu_thread(executeSBM_CPU);
thread gpu_thread(executeSBM_GPU);
/* Wait for thread termination. */
cpu_thread.join();
gpu_thread.join();
/* Check the time at end. */
high_resolution_clock::time_point t2 = high_resolution_clock::now();
/* Indicate that this sequence is finished. */
is_sequence_finished.store(true);
/* Wait for thread exiting. */
power_measure_thread.join();
/* Calculate results. (millisecond) */
duration<double> time_span = duration_cast< duration<double> >(t2 - t1);
int total_time = (int)(time_span.count() * 1000);
cout << "elapsed time: " << total_time << "ms" << endl;
double processed_image_per_second = (double)NUM_OF_ITERATION / ((double)total_time / 1000.0);
cout << "processed image per second: " << processed_image_per_second << endl;
cout << "VDD_SYS_GPU: " << get<0>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
cout << "VDD_SYS_SOC: " << get<1>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
cout << "VDD_4V0_WIFI: " << get<2>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
cout << "VDD_IN: " << get<3>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
cout << "VDD_SYS_CPU: " << get<4>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
cout << "VDD_SYS_DDR: " << get<5>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
cout << "VDD_MUX: " << get<6>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
cout << "VDD_5V0_IO_SYS: " << get<7>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
cout << "VDD_3V3_SYS: " << get<8>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
cout << "VDD_3V3_IO_SLP: " << get<9>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
cout << "VDD_1V8_IO: " << get<10>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
cout << "VDD_3V3_SYS_M2: " << get<11>(power_results) << "mW" << endl;
double power_sum = get<0>(power_results) + get<1>(power_results) + get<2>(power_results) + get<3>(power_results);
power_sum += get<4>(power_results) + get<5>(power_results) + get<6>(power_results) + get<7>(power_results);
power_sum += get<8>(power_results) + get<9>(power_results) + get<10>(power_results) + get<11>(power_results);
cout << "Sum of power: " << power_sum << "mW" << endl;
cout << "Power To Performance: " << processed_image_per_second / (power_sum / 1000) << " (processed_image_per_sec/W)" << endl;
}
My code requires OpenCV(version 2.4) Library.
In TX2, you can use OpenCV4Tegra, which can be installed using JetPack.
To use this code, please prepare 2 images which have same image type, same resolution.
Above code uses both CPU and GPU.
Therefore, if you want to use only CPU or GPU, please comment line number 189 (for disable CPU) or line number 190 (for disable GPU).